|
|
|
The Titan I was deployed in a 3x3
configuration, meaning a squadron of nine missiles was divided into
three, three-missile launch complexes. In 1956 the Air Force decided
that all of the Titan I missiles should be based in super-hardened"
silos buried deep underground. Using data from above-ground nuclear
tests, the Air Force found that at a reasonable cost it could
construct the launch facilities to withstand overpressures of 25 to
100 pounds per square inch (psi).
Subsequently, all of the Titan I launch sites were built to withstand
overpressures of 100 psi. |
|
 |
The Army Corps
of Engineers Ballistic Missile Construction Office began building the first Titan I launch
facilities at Lowry AFB, Colorado, in May 1959. Each squadron consisted of
nine missiles evenly divided among three launch complexes. The missiles
were grouped in clusters of three because they had to remain close to
their ground-based radars and guidance computers.
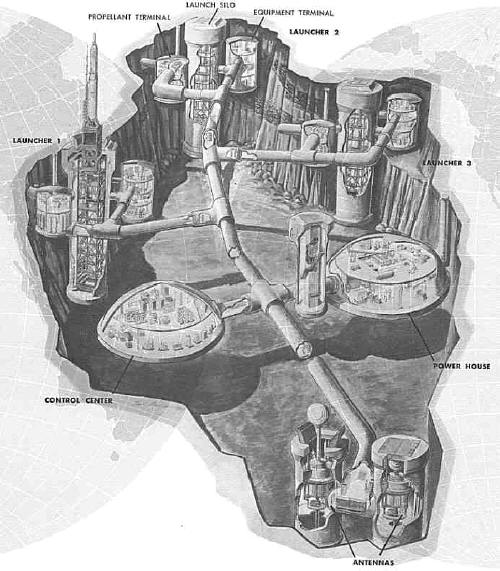
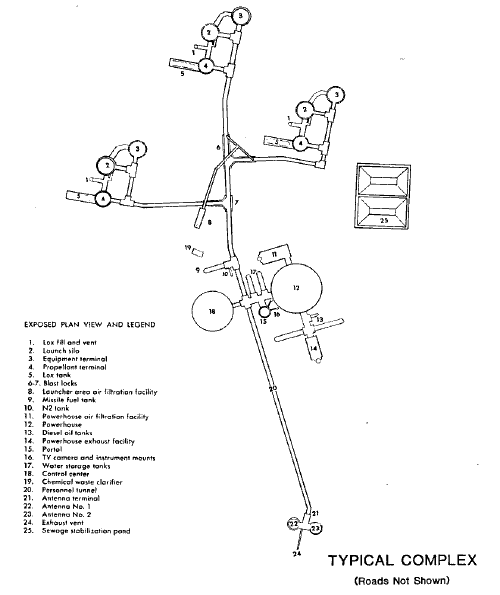
The mammoth underground complexes were miniature
cities, complete with their own power and water supplies. The entire
complex was buried deep beneath the ground, and all the parts were linked
by underground passageways. At one end of the complex were the three
missile silos, each 160 feet deep and 44 feet in diameter. They were built
of reinforced concrete that ranged in thickness from 2 to 3 feet. Within
the silo was a steel framework that housed both the missile and the
elevator that carried it to the surface. The only parts of the silo that
protruded above the surface were two horizontal doors, each weighing 125
tons.
Adjacent to each silo were the propellant storage and
equipment terminal buildings, both of which were buried under 17 to 24
feet of earth. Several hundred feet away were the control room and power
house. Both were domed structures built of reinforced concrete and buried
10 to 17 feet beneath the surface. The control room was 40 feet high,100
feet in diameter, and housed all of the launch control equipment. The
nearby power house was 60 feet high, 127 feet in diameter, and contained
generators and the power distribution system. Nestled between the two
buildings was the cylindrical entry portal,72 feet deep and 38 feet in
diameter, that controlled access to the underground complex.
At the base of the complex were two radar
antennas that were part of the missile's ground-based guidance system. The
antennas were housed in two silos, each 67 feet deep and 38 feet in
diameter. The launch crews raised tfie antennas above ground as they
readied the missile for firing. The antennas were approximately 1,300 feet
from the farthest silo. More than 2,500 feet of corrugated steel tunnel, 9
feet in diameter and buried 40 feet beneath the surface, connected all the
buildings within the complex. |
|
 |
| |
|
